Connecting Wallets & Authenticating
Stacks.js starters offer working templates with Stacks Connect pre-installed for a quick and easy way to get started with building Stacks enabled web apps.
This guide explains how to connect to users' wallets and authenticate users with the @stacks/connect package of Stacks.js.
Installing Dependency
To install the @stacks/connect package in your JavaScript/TypeScript project, run:
npm install @stacks/connect
Authentication
Authentication allows users to identify themselves in an app while retaining complete control over their credentials and personal details. This package can be integrated alone or used in conjunction with transaction signing and data storage. The authentication package is a prerequisite for using these latter two packages.
Users who register for your app can subsequently authenticate to any other app with support for the Blockchain Naming System and vice versa.
Initiate userSession
Apps keep track of user authentication state with the userSession object, initiated with the UserSession and AppConfig classes:
import { AppConfig, UserSession } from '@stacks/connect';
const appConfig = new AppConfig(['store_write', 'publish_data']);
const userSession = new UserSession({ appConfig });
The main thing to decide here is what permission scopes your app needs from the user during authentication.
Apps may request any of the following scopes:
| Scope | Definition |
|---|---|
store_write | Read and write data to the user's Gaia hub in an app-specific storage bucket. |
publish_data | Publish data so other app users can discover and interact with the user. |
The default scopes are ['store_write'] if no scopes array is provided when initializing the appConfig object.
We recommend you initiate the userSession object just once in your app and then reference it using imports where needed.
Initiate Authentication Flow
Apps prompt both new and existing users to authenticate with the showConnect function:
import { AppConfig, UserSession, showConnect } from '@stacks/connect';
const appConfig = new AppConfig(['store_write', 'publish_data']);
const userSession = new UserSession({ appConfig });
function authenticate() {
showConnect({
appDetails: {
name: 'My App',
icon: window.location.origin + '/my-app-logo.svg',
},
redirectTo: '/',
onFinish: () => {
let userData = userSession.loadUserData();
// Save or otherwise utilize userData post-authentication
},
userSession: userSession,
});
}
showConnect triggers the display of a popup that initiates the authentication process for users, one in which they'll authenticate with a Secret Key that's used to encrypt their private data.
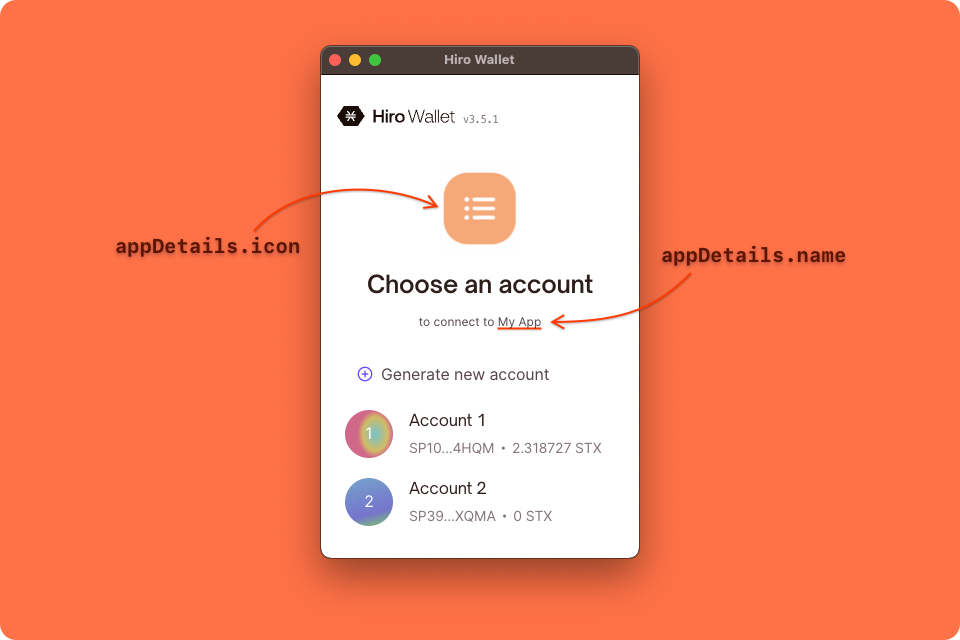
The showConnect function accepts a several properties within a parameter object, such as:
- The app's
nameandiconare provided as strings comprising theappDetailsobject property. - The
redirectTostring is used to provide a URL to which the user should be redirected upon successful authentication. TheonFinishcallback serves a similar purpose by handling successful authentication within the context of a popup window. - The
userSessionobject initiated above.
Once the user selects the button in this popup, they are passed to the Stacks Wallet for authenticator with the authRequest token as a GET parameter. From there, they can confirm authentication and generate a new Secret Key or Stacks identity before doing so, as needed, before coming back to the app.
Handle Pending Authentication
Unless the user has confirmed authentication within the context of a popup window, they will get redirected back to the app via the redirectTo address provided above, at which point the app needs to handle the pending authentication state using the authResponse value provided as a GET parameter:
import { AppConfig, UserSession, showConnect } from '@stacks/connect';
const appConfig = new AppConfig(['store_write', 'publish_data']);
const userSession = new UserSession({ appConfig });
window.onload = function () {
if (userSession.isSignInPending()) {
userSession.handlePendingSignIn().then(userData => {
// Save or otherwise utilize userData post-authentication
});
} else if (userSession.isUserSignedIn()) {
// Handle case in which user is already authenticated
}
};
The isSignInPending method of the userSession object detects whether the user needs to handle a pending authentication state upon page load.
The handlePendingSignIn method is then used to handle that state, returning a userData object with all the data needed to save the user's information into their session.
The authenticated state can later be detected by the isUserSignedIn method in case any particular handling is needed.
It's essential to implement handlePendingSignIn within the context of mobile apps.
If the user has indeed confirmed authentication in the context of a popup window, the authenticator will resolve the pending authentication state automatically with the app within the parent window.
It will then trigger the onFinish function provided above, which can be used similarly to save the user's information into their session as retrieved with userSession.loadUserData().
Advanced
How It Works
The authentication flow with Stacks is similar to the typical client-server flow used by centralized sign in services (for example, OAuth). However, with Stacks, the authentication flow happens entirely client-side.
An app and authenticator, such as the Stacks Wallet, communicate during the authentication flow by passing back and forth two tokens. The requesting app sends the authenticator an authRequest token. Once a user approves authentication, the authenticator responds to the app with an authResponse token.
These tokens are based on a JSON Web Token (JWT) standard with additional support for the secp256k1 curve used by Bitcoin and many other cryptocurrencies. They are passed via URL query strings.
See the authRequest and authResponse payload schemas below for more details about what data they contain.
When a user chooses to authenticate an app, it sends the authRequest token to the authenticator via a URL query string with an equally named parameter:
https://wallet.hiro.so/...?authRequest=j902120cn829n1jnvoa...
When the authenticator receives the request, it generates an authResponse token for the app using an ephemeral transit key . The ephemeral transit key is just used for the particular instance of the app, to sign the authRequest.
The app stores the ephemeral transit key during request generation. The public portion of the transit key is passed in the authRequest token. The authenticator uses the public portion of the key to encrypt an app private key , which is returned via the authResponse.
The authenticator generates the app private key from the user's identity address private key , and the app's domain. The app's private key serves three functions:
- It is used to create credentials that give the app access to a storage bucket in the user's Gaia hub
- It is used in the end-to-end encryption of files stored for the app in the user's Gaia storage.
- It is a cryptographic secret that apps can use to perform other cryptographic functions.
Finally, the app private key is deterministic, meaning that the same private key will always be generated for a given Stacks address and domain.
The first two functions are particularly relevant to data storage with Stacks.js.
Learn more about keypairs used by authentication.
Key Pairs
Authentication with Stacks makes extensive use of public key cryptography and ECDSA with the secp256k1 curve in particular.
The following sections describe the three public-private key pairs used, including how they're generated, where they're used and to whom private keys are disclosed.
Transit Private Key
The transit private is an ephemeral key used to encrypt secrets that need to be passed from the authenticator to the app during the authentication process. It is randomly generated by the app at the beginning of the authentication response.
The public key corresponding to the transit private key is stored in a single
element array in the public_keys key of the authentication request token. The
authenticator encrypts secret data such as the app's private key using this
public key and sends it back to the app when the user signs in to the app. The
transit private key signs the app authentication request.
Identity Address Private Key
The identity address private key is derived from the user's keychain phrase and is the private key of the Stacks username the user chooses to use to sign in to the app. It is a secret the user owns and never leaves the user's instance of the authenticator.
This private key signs the authentication response token for an app to indicate that the user approves signing in to that app.
App Private Key
The app private key is an app-specific private key generated from the
user's identity address private key using the domain_name as input.
The app private key is securely shared with the app on each authentication, encrypted by the authenticator with the transit public key. Because the transit key is only stored on the client side, this prevents a man-in-the-middle attack where a server or internet provider could snoop on the app private key.
authRequest Payload Schema
const requestPayload = {
jti, // UUID
iat, // JWT creation time in seconds
exp, // JWT expiration time in seconds
iss, // legacy decentralized identifier generated from transit key
public_keys, // single entry array with public key of transit key
domain_name, // app origin
manifest_uri, // url to manifest file - must be hosted on app origin
redirect_uri, // url to which the authenticator redirects user on auth approval - must be hosted on app origin
version, // version tuple
do_not_include_profile, // a boolean flag asking authenticator to send profile url instead of profile object
supports_hub_url, // a boolean flag indicating gaia hub support
scopes, // an array of string values indicating scopes requested by the app
};
authResponse Payload Schema
const responsePayload = {
jti, // UUID
iat, // JWT creation time in seconds
exp, // JWT expiration time in seconds
iss, // legacy decentralized identifier (string prefix + identity address) - this uniquely identifies the user
private_key, // encrypted private key payload
public_keys, // single entry array with public key
profile, // profile object
username, // Stacks username (if any)
core_token, // encrypted core token payload
email, // email if email scope is requested & email available
profile_url, // url to signed profile token
hubUrl, // url pointing to user's gaia hub
version, // version tuple
};
Decode authRequest or authResponse
To decode a token and see what data it holds:
Copy the
authRequestorauthResponsestring from the URL during authentication.Navigate to jwt.io.
Paste the full token there.
The output should look similar to the below:
{
"jti": "f65f02db-9f42-4523-bfa9-8034d8edf459",
"iat": 1555641911,
"exp": 1555645511,
"iss": "did:btc-addr:1ANL7TNdT7TTcjVnrvauP7Mq3tjcb8TsUX",
"public_keys": ["02f08d5541bf611ded745cc15db08f4447bfa55a55a2dd555648a1de9759aea5f9"],
"domain_name": "http://localhost:8080",
"manifest_uri": "http://localhost:8080/manifest.json",
"redirect_uri": "http://localhost:8080",
"version": "1.3.1",
"do_not_include_profile": true,
"supports_hub_url": true,
"scopes": ["store_write", "publish_data"],
"private_key": "4447bfa55a55a2dd555648a1d02f08d759aea5f945cc15db08f"
}The
issproperty is a decentralized identifier ordid. This identifies the user and the username to the app. The specificdidis abtc-addr.